If you look at it a little bit, you can see that the antenna towers are all high around you, or you can just put a signal tower on a local high-rise.
I never knew why I had to do this before, but I took it for granted.
However, after learning the principle of communication recently, the reason why the antenna tower is relatively high can be understood.
Under the understanding of sight distance propagation
Line-of-sight propagation (LOS propagation) refers to the propagation of space wave between two points that can be directly reached when ultra-short wave and microwave are used for ground communication and broadcasting. Its distance is similar to that of the people on the ground, and generally does not exceed 50km.
High-frequency (2MHz ~ 30MHz) electromagnetic waves, known as high-frequency electromagnetic waves, can penetrate the lowest atmospheric ionosphere, but will be reflected back to the ground by the upper ionosphere, the ground will reflect the electromagnetic waves back to the atmosphere, thus producing the mode of sky wave propagation.
Electromagnetic waves with frequencies higher than 30MHz penetrate the ionosphere directly. The signals of our mobile phones are ultrashort waves, and the frequencies are much higher than 30MHz.
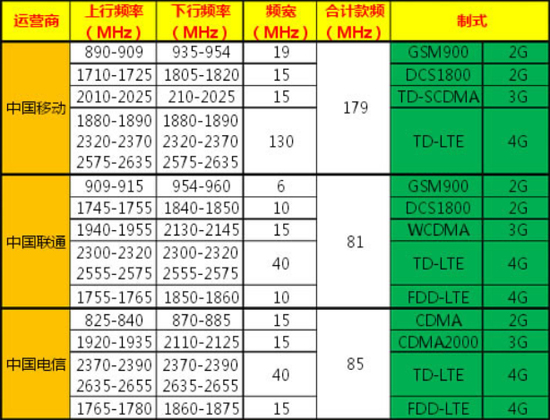
Therefore, the transmission of mobile phone signals belongs to the line of sight propagation.
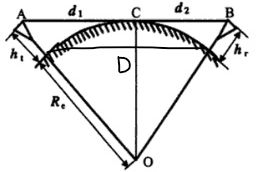
The antenna height is equal to h, the earth radius R is 6370km, and the Pythagorean theorem shows that:
D2+R2= (h+R) 2
be
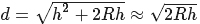
D is two antenna distance.
D2= (2D) 2=8Rh
Bring the value of R into the upper form.
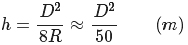
Formula: D for transmit receive antenna distance (km)
Further explanation of tower height
Generally, the distance between transmit and receive antennas is between 20km and 50km. Many factors are taken into account, such as high cost of tower, long distance, high power and high electricity cost.
The distance D of the line-of-sight transmission is 50 km, and the height h of the antenna is 50 m.
Therefore, the antenna tower is always high. (nodding manually)
Knowledge extension
From the above we know that the normal distance of sight distance propagation is 50km. What about long-distance transmission? This can be achieved by wireless relay.
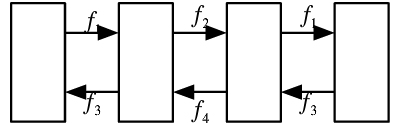
四频制
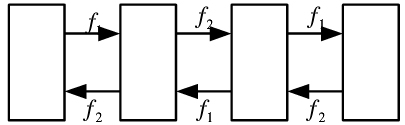
二频制
In the case of the LOS propagation distance of 50 km, an antenna tower can be built every 50 km, and then the signal is transmitted every 50 km. And each tower receives and sends different frequencies, otherwise mixing problems will occur, resulting in the signal can not be restored.
From the deduction of the formulas above, we can see that the distance of LOS propagation is related to the height of the antenna. If we want to make the distance of LOS propagation farther, we need to set up a higher antenna. But considering the cost of the antenna tower, it is difficult to complete on the ground, so we can consider to let the antenna go to the sky and use the satellite as the rotation. The station (base station) is also called satellite communication.
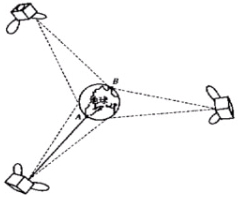
However, the delay of satellite communication is relatively high, and the cost of satellite is not low, after all, it is not easy to go to heaven. The stratospheric communication is currently developing to solve this delay problem.
This project is called the air base station, and now some large companies such as Google and Facebook are doing this project. The advantages of using aerial base stations are obvious, avoiding artificial laying of infrastructure such as fiber optic networks, low cost, and no need to worry about human destruction.
But there are still many problems in the air base station, such as how to maintain a stable high bandwidth, how to maintain a reliable network environment, these are very big problems, because the air base station in the stratosphere, will be affected by the weather, the air base station wireless network technology needs to rely on microwave, millimeter wave or FSO (since) It is implemented by a space optical communication system, but microwaves have relatively low capacitance; millimeter and FSO are often affected by weather (millimeter waves do not work properly in cloudy and rainy weather, and FSO performance is affected by dust and fog). And there's also the problem of unfixed displacement in the air base station, which is caused by the Earth's rotation. This is a very big problem. If two wireless transceivers are five miles apart, and one of them deviates from the normal position by only one degree, the final signal will reach a target position that is nearly 500 feet offset from the original position.